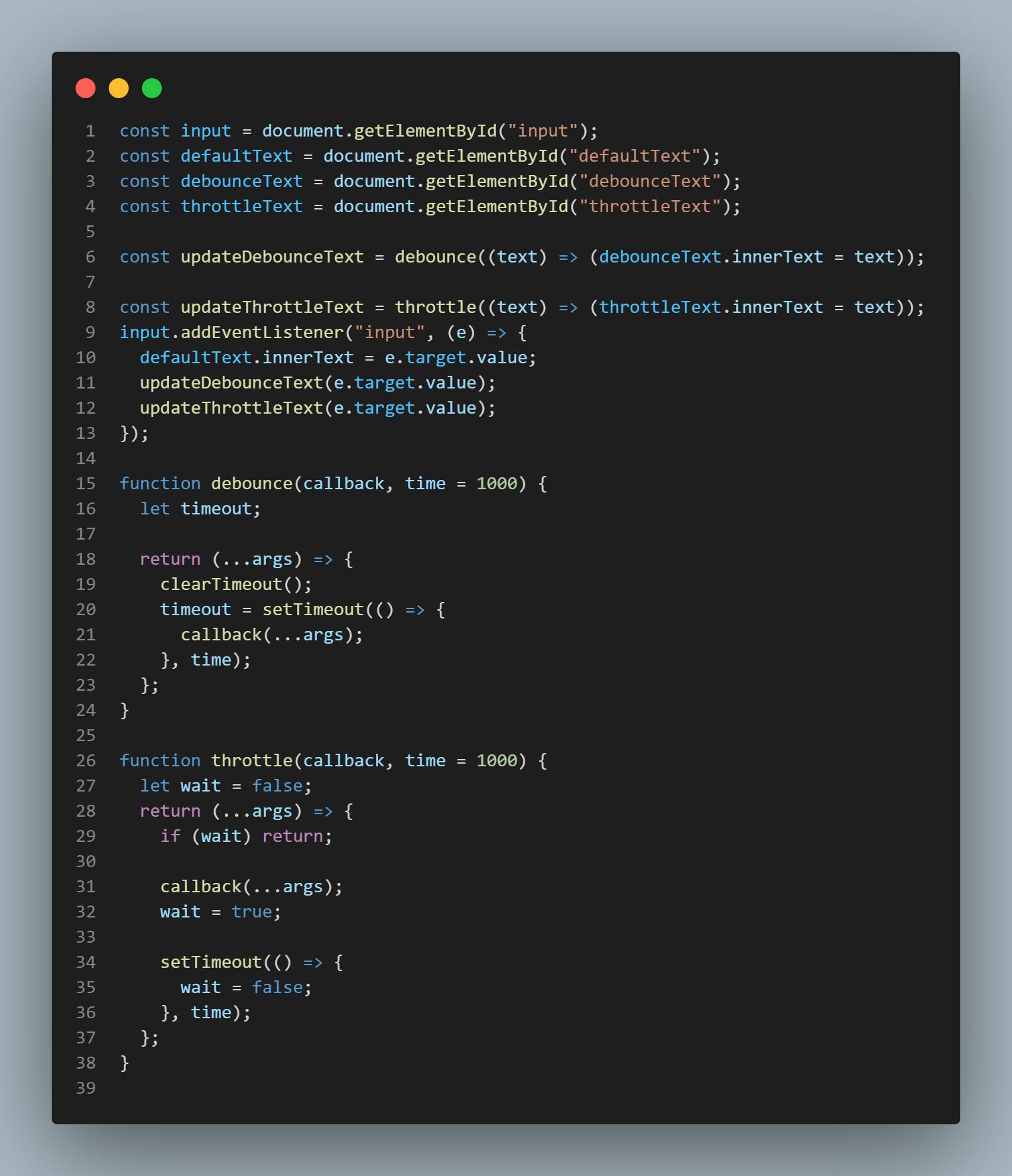
Debouncing and Throttling are techniques used in JavaScript to control the frequency at which an event or function is executed.
Debouncing is a technique that delays the execution of a function until a certain period of time has passed after the last time the function was called. This helps to reduce the number of times a function is executed and can be useful when dealing with rapidly firing events, such as window resizing or scrolling events.
For example, if you have an event handler attached to the window.resize event that updates the layout of your page every time the window is resized, you may want to use debouncing only to update the layout once every 500 milliseconds after the window has finished being resized.
Throttling, on the other hand, is a technique that limits the number of times a function can be executed within a specified time interval. It's similar to debouncing, but it limits the number of executions to a fixed number, rather than delaying the execution until after a certain period of time has passed.
For example, suppose you have an event handler attached to the scroll event that updates the position of an element as the user scrolls. In that case, you may want to use throttling to only update the position of the element once every 10 milliseconds, regardless of how many times the event fires.
Debouncing and Throttling are commonly used in web development to optimize the performance of web pages and improve the user experience by avoiding unnecessary calculations and DOM updates. They are used in various JavaScript frameworks, libraries, and plugins to control the execution of functions in response to events.